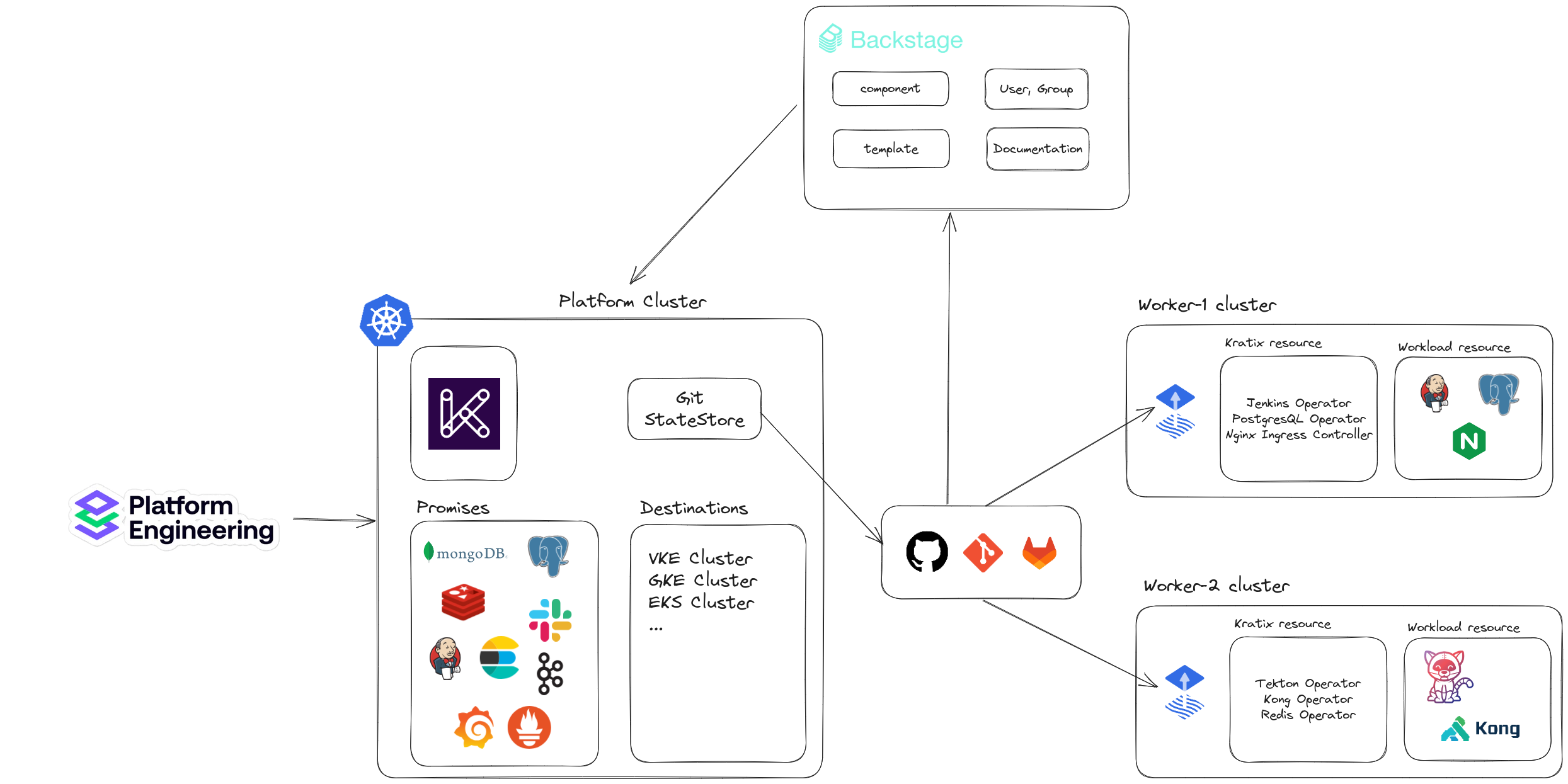
1. Deploy Kratix in a multi-cluster model (platform - workers)
2. Install necessary tools
3. Deploy Platform cluster
Create the platform cluster using kind
kind create cluster --image kindest/node:v1.27.3 --name platform export PLATFORM="kind-platform"Install cert-manager on the platform cluster
kubectl --context $PLATFORM apply -f https://github.com/cert-manager/cert-manager/releases/download/v1.12.0/cert-manager.yamlInstall kratix on the platform cluster
kubectl apply --context $PLATFORM --filename https://github.com/syntasso/kratix/releases/latest/download/kratix.yamlConfigure State Store for Kratix
Kratix uses GitOps to provide resources on the worker cluster. We can configure Kratix with multiple GitOps repositories by creating a State Store. Kratix supports Bucket State Store and Git State Store.
Here we will use Git State Store. When using GitStateStore, we need to give Kratix permission to push resources to the repository by creating a token or providing user password via secret in K8S.
Github Token:
kubectl apply --context $PLATFORM --filename github-secret.yamlgithub-secret.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: github-secret type: Opaque data: username: [username base64] password: [password base64]Configure GitStateStore for Kratix:
kubectl apply --context $PLATFORM --filename platfom_v1alpha1_gitstatestore.yamlplatfom_v1alpha1_gitstatestore.yamlapiVersion: platform.kratix.io/v1alpha1 kind: GitStateStore metadata: name: default spec: path: kratix/ secretRef: name: github-secret namespace: default url: https://github.com/Choco-Boba/backstage branch: main
4. Deploy Worker clusters:
Create the worker cluster using kind:
kind create cluster --image kindest/node:v1.27.3 --name worker export WORKER="kind-worker"Install Flux on the worker cluster:
kubectl apply --context $WORKER --filename https://raw.githubusercontent.com/syntasso/kratix/main/hack/destination/gitops-tk-install.yamlConfigure Flux for the worker cluster
We configure the storage location for resources so that Flux can synchronize and deploy resources on the worker cluster:
Requirements:
Secret storing Github/Gitlab token or username password. Refer to: https://docs.kratix.io/main/reference/statestore/gitstatestore#auth
flux_worker_1.yamlapiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1 kind: GitRepository metadata: name: kratix-workload-resources namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 5s url: https://github.com/Choco-Boba/backstage ref: branch: main secretRef: name: github-secret --- apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization metadata: name: kratix-workload-resources namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 3s dependsOn: - name: kratix-workload-dependencies sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: kratix-workload-resources path: "kratix/worker-1/resources/" prune: true --- apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1 kind: GitRepository metadata: name: kratix-workload-dependencies namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 5s url: https://github.com/Choco-Boba/backstage ref: branch: main secretRef: name: github-secret --- apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization metadata: name: kratix-workload-dependencies namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 8s sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: kratix-workload-dependencies path: "kratix/worker-1/dependencies/" prune: trueFinally, register the worker cluster with the platform cluster where Kratix is installed. See more at https://docs.kratix.io/main/reference/destinations/intro
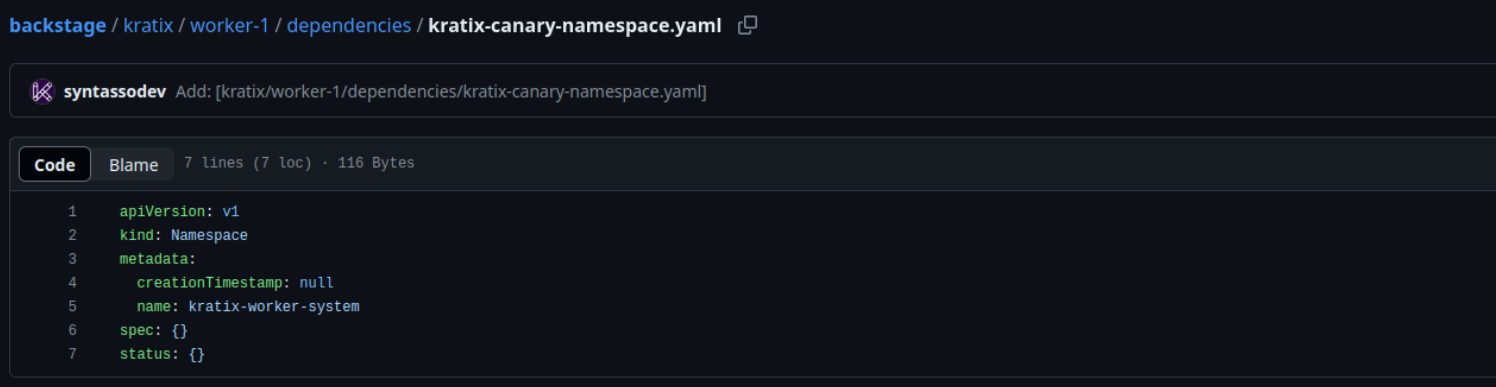
kubectl apply --context $PLATFORM --filename platform_v1alplha1_worker.yamlplatform_v1alplha1_worker.yamlapiVersion: platform.kratix.io/v1alpha1 kind: Destination metadata: name: worker-1 labels: environment: dev spec: stateStoreRef: name: default kind: GitStateStoreAfter registering the worker cluster with the platform cluster, Kratix will start pushing the first resource (namespace kratix-worker-system) to the folder of the worker cluster (just registered) on the git repository.
The folder of the cluster will be named according to the Destination name:
Other worker clusters that want to join will also follow the same steps from installing Flux.
5. Install Promises on the Platform cluster (Example Jenkins)
We can find Promise resources on the Kratix Marketplace or write our own Promises: Kratix Marketplace
Jenkins Promise: https://github.com/syntasso/kratix-marketplace/tree/main/jenkins
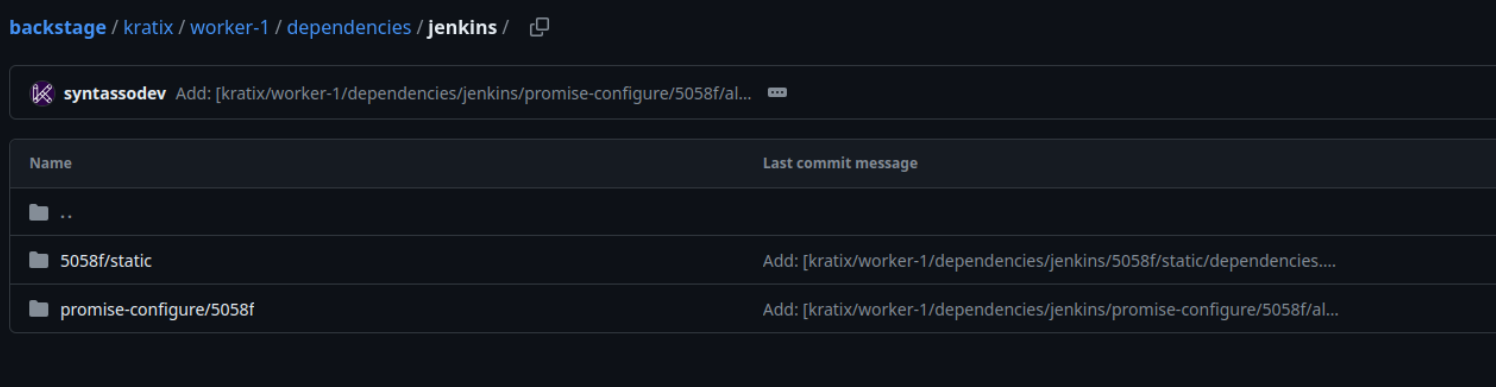
kubectl apply --context $PLATFORM --filename promise.yamlAfter installing the Jenkins Promise on the Platform cluster, Kratix will start pushing resources to the folder of the registered worker cluster.
Then the worker cluster will synchronize from the git repository and deploy the necessary resources that Kratix has requested.
Here with the Jenkins Promise, Kratix will push the resource dependencies, which is a Jenkins Operator, to the worker cluster.
Each time a Jenkins instance is requested, the Jenkins Operator will create this resource on the worker cluster.
6. Conclusion
- With the Kratix multi-cluster deployment model (platform - workers), we can easily scale the worker cluster without affecting the platform cluster. The platform cluster will manage and provide resources for the worker cluster through GitOps. The worker cluster will synchronize and deploy the resources requested by the platform cluster.
- This Platform Orchestrator model is quite interesting but requires the worker clusters to install the necessary resources as mentioned above. We will compare it with another Platform Orchestrator in the next blog post.
NOTE
Checkout up coming talk about Platform Orchestrator at FOSSASIA Summit 2025.