1. Introduction
Danh sách liên kết là một cấu trúc dữ liệu tuyến tính, trong đó các phần tử không được lưu trữ tại các vị trí bộ nhớ liền kề. Các phần tử trong danh sách được liên kết được liên kết bằng cách sử dụng con trỏ như được hiển thị trong hình ảnh bên dưới:
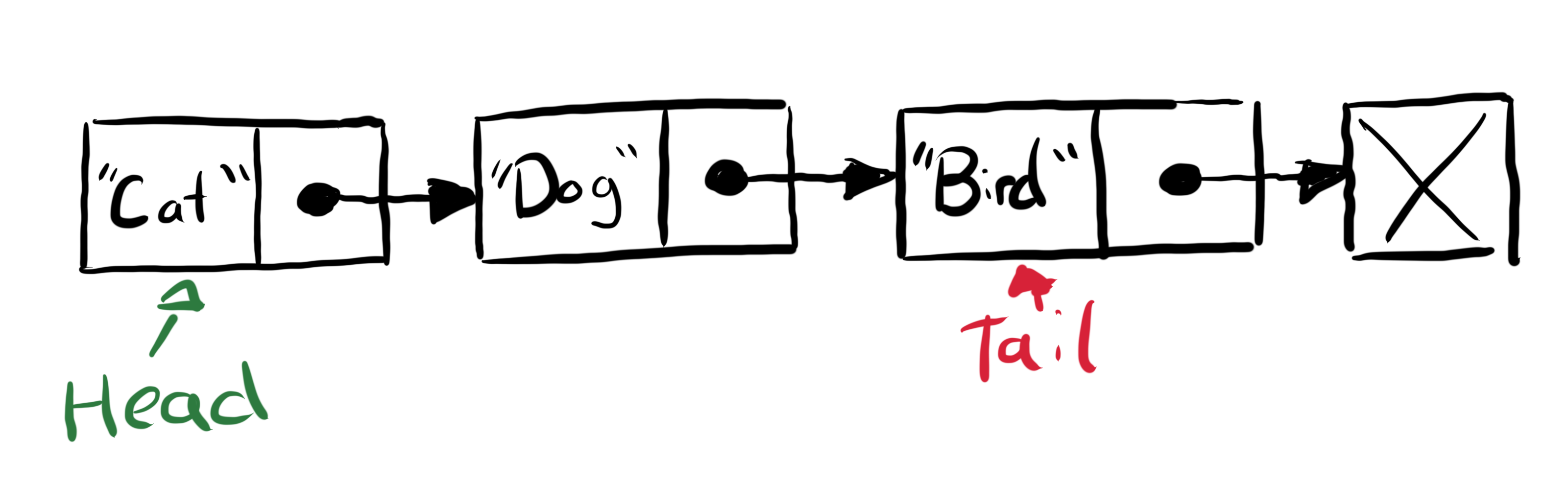
Figure 1: Linked List Diagram
Bắt đầu với cấu trúc đơn giản nhất
struct Node {
int data;
Node *next;
};
Trong hàm main ta khai báo như sau:
int main() {
Node *one = new Node();
Node *two = new Node();
Node *three = new Node();
// Set one is head
Node *head = one;
// Set value
one->data = 1;
two->data = 2;
three->data = 3;
// Link
one->next = two;
two->next = three;
// head -> next -> next
// one -> two -> three
}
Như vậy chúng ta đã có một list. Giờ chúng ta muốn thêm một phần tử zero vào một vị trí bất kì thì làm thế nào?
2. Thêm phần tử vào đầu danh sách liên kết
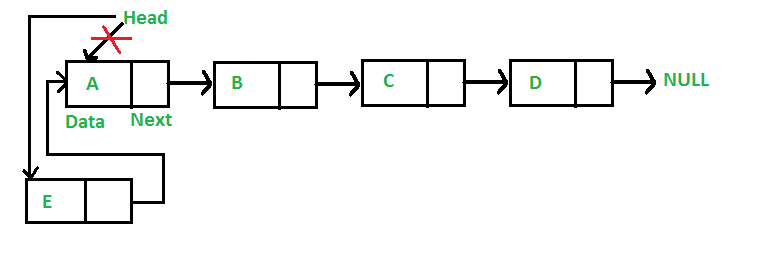
Figure 2: Add Node to Head
2.1. Code
void addhead(int data, Node **head) {
Node* new_head = new Node();
new_head->data = data;
new_head->next = *head;
*head = new_head;
}
2.2. Test
int main() {
...
addhead(0, &head); // set head->data = 0
cout << head->data; // head->data = 0
}
Cho những bạn chưa hiểu tại sao trong hàm addhead(0, &head), &head ở đây có nghĩa chúng ta đang cho vào địa trỉ của một biến con trỏ.
Chúng ta đưa vào địa trỉ để thay đổi giá trị nó, cái này gọi là tham chiếu, còn nếu là Node *head thì chỉ truyền vào giá trị, ta không thay đổi được sau khi kết thúc hàm, đó gọi là tham trị.
3. Thêm sau một vị trí cho trước
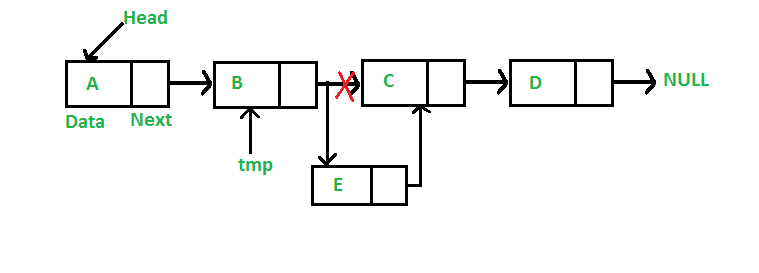
Figure 3: Add Node After
3.1. Code
void insertAfter(Node *index, int data) {
if (index == NULL) return;
Node *new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = index->next;
index->next = new_node;
}
Phần này khá dễ hiểu mọi người hãy nhìn hình Figure 3 sẽ hiểu.
4. Thêm vào cuối danh sách
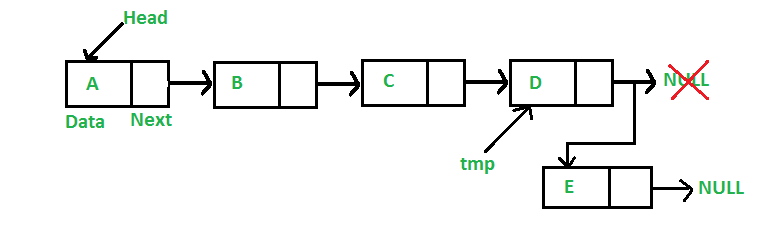
Figure 4: Add Node to Tail
4.1. Code
void append(Node **head, int data) {
Node *new_node = new Node();
new_node->data = data;
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = new_node;
return;
}
Node *tmp = *head;
while(tmp->next != NULL) {
tmp = tmp->next;
}
tmp->next = new_node;
}
4.2. Test
void printlist(Node *node) {
while(node) {
cout << node->data << " ";
node = node->next;
}
}
int main() {
Node *head = NULL;
append(&head, 0);
append(&head, 1);
append(&head, 2);
append(&head, 3);
append(&head, 4);
printlist(head);
return 0;
}
Kết quả sẽ là 0 1 2 3 4.
5. Xóa phần tử có giá trị bằng x
Cho một Linked List chúng ta hay xóa phần tử có
5.1. Code
void delete_value(Node **head, int x) {
Node *tmp = *head;
Node *prev = NULL;
if (*head == NULL) return;
if (tmp->data == x) {
*head = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
} else {
while(tmp->data != x) {
prev = tmp;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
prev->next = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
}
}
6. Xóa phần tử tại vị trí cho trước
6.1. Code
void delete_pos(Node **head, int pos) {
if (*head == NULL) return;
Node *tmp = *head;
if(pos == 0) {
*head = tmp->next;
delete tmp;
return;
}
pos--;
while(pos--) {
tmp = tmp->next;
}
Node *aft = tmp->next->next;
delete tmp->next;
tmp->next = aft;
}
Xem hoạt ảnh sau để có thể dễ dàng hiểu:
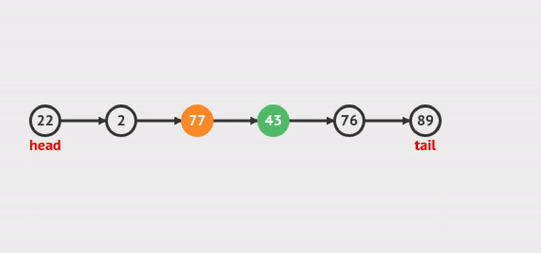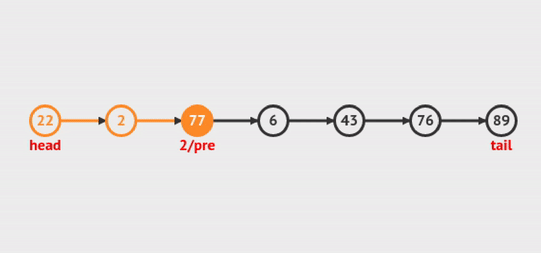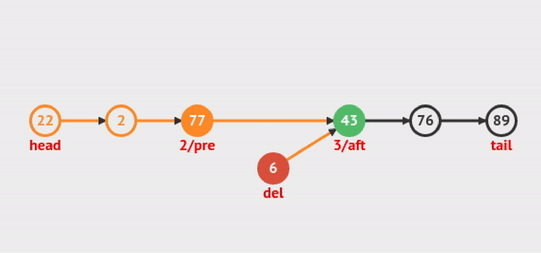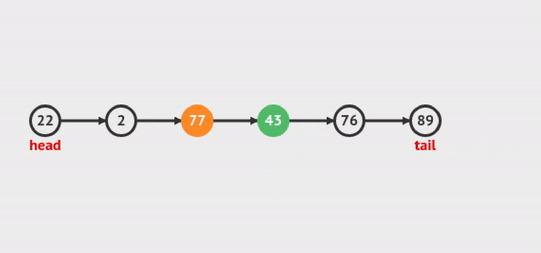
Figure 5: Delete Node at Index
7. Xóa một Linked List?
7.1. Code
void delete_list(Node **head) {
Node *curr = *head;
Node *next = NULL;
while(curr) {
next = curr->next;
delete curr;
curr = next;
}
*head = NULL;
}
8. Tìm độ dài của Linked List
8.1. Code
int len_list(Node *head) {
if (head == NULL) return 0;
int len = 0;
while(head) {
len++;
head = head->next;
}
return len;
}
Ở đây chúng ta chỉ cần xét giá trị không cần thiết phài Node **head để truy đến địa trỉ, chúng ta chỉ cần biến đếm và không cần thay đổi giá trị gì cả 😙.
9. Check xem trong Linked List có giá trị nào bằng x không:
9.1. Code
bool find(Node *head, int x) {
while(head) {
if (head->data == x) return true;
head = head->next;
}
return false;
}
10. Lấy giá trị tại vị trí cho trước
10.1. Code
int getNth (Node *head, int index) {
int len = len_list(head);
if (index > len) return -1;
while(index--) {
head = head->next;
}
return head->data;
}
11. Tìm độ dài của LOOP trong Linked List
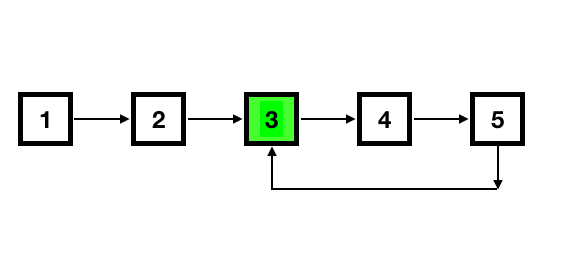
Figure 6: Find Loop Length
11.1. Đầu tiên hay tìm hiểu cách kiểm tra xem có loop trong linked list hay không?
bool loopDetect(Node *head) {
Node *fast = head;
Node *slow = head;
while (fast && slow && fast->next) {
if (fast == slow) return true;
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return false;
}
Ta cho slow, fast chạy cho đến khi hai con trỏ bằng nhau thì chứng tỏ có LOOP. Dễ hiểu đúng không?
Còn một cách nữa là sử dụng Set:
bool loopDetect(Node *head) {
set<Node *> s;
while(head) {
if (s.find(head) != s.end()) {
return true;
} else {
s.insert(head);
head = head->next;
}
}
return false;
}
11.2. Tìm độ dài của LOOP
Chúng ta đã có cách kiểm tra và biết vị trí LOOP chính là tại slow || fast tại thời điểm nó bằng nhau. Giờ hay tiếp với hàm tìm độ dài của LOOP này.
int countFrom(Node *loopIndex) {
int len = 1;
Node *tmp = loopIndex;
while(tmp->next != loopIndex) {
len++;
tmp = tmp->next;
}
return len;
}
Hàm countFrom là hàm đếm độ dài và input là con trỏ tại vị trí có LOOP, tức là vị trí end->next, đã đi đến đây thì bạn sẽ dễ dàng hiểu được hàm.
int countLoop(Node *head) {
Node *slow = head;
Node *fast = head;
while (slow && fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (fast == slow) {
return countFrom(slow);
// or return countfrom(fast);
}
}
return 0;
}
12. Xóa phần tử lặp của một Linked List chưa được sắp xếp:
12.1. Code
void removeDuplicates (Node **head) {
Node *curr = *head;
Node *prev = NULL;
unordered_set<int> s;
while(curr) {
if (s.find(curr->data) != s.end()) {
prev->next = curr->next;
delete curr;
} else {
s.insert(curr->data);
prev = curr;
}
curr = prev->next;
}
// do phuc tap la O(n)
}
Ta sẽ sử dụng Hashing để có thể có độ phức tạp là .
13. Intersection of Two Linked Lists (LeetCode) | Giao điểm của hai danh sách được liên kết.
13.1. Code
Node *getIntersectionNode (Node *headA, Node *headB) {
set<Node *> s;
while(headA) {
s.insert(headA);
headA = headA->next;
}
while(headB) {
if (s.find(headB) != s.end()) {
return headB;
} else {
s.insert(headB);
headB = headB->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
14. Reverse Linked Lists (LeetCode) | Đảo ngược Linked List
14.1. Code
Node *reverseList(Node **head) {
Node *curr = *head;
Node *prev = NULL;
while (curr) {
Node *tmp = curr->next;
curr->next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = tmp;
}
return prev;
}
- Time complexity : . Assume that is the list's length, the time complexity is .
- Space complexity : .
15. Remove Elements (LeetCode)
15.1. Code
Node *removeElements(Node **head, int value) {
Node *curr = head;
Node *prev = new Node();
prev->next = head;
// prev slower than curr 1 step
while(curr) {
if(curr->value == value) {
prev->next = curr->next;
} else {
prev = prev->next;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
return *head;
}
16. Odd Even
Figure 7: Odd Even Linked List
Ở đây bài toán mặc định phần tử đầu tiên là lẻ, phần tử thứ hai là chẵn, ta sẽ giải quyết theo hướng chia ra làm hai list rồi nối chúng lại với nhau.
16.1. Code
Node *oddevenList(Node **head) {
Node *odd = *head;
Node *even = odd->next;
Node *evenHead = even;
while(even && even->next) {
odd->next = even->next;
odd = odd->next;
even->next = odd->next;
even = even->next;
}
odd->next = evenHead;
return *head;
}
NOTE
To be updated